Brain Assessment Overview
Dr. Hugh's Guide to Understanding the Brain Assessment Form
Introduction
If you’ve recently filled out the brain assessment form, this guide will help you understand what the different assessments mean and what they might mean for your case. This information should provide an understanding of the degree of any neuroinflammation or brain problems you may have and the potential corrective actions that can be taken.
Brain Structure Overview
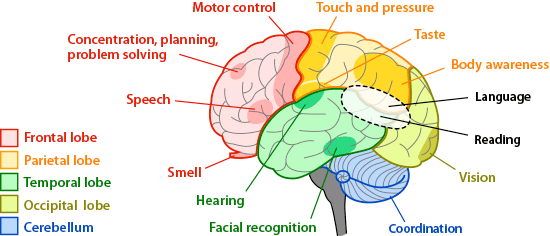
1. Frontal Lobe:
- Location: At the front, near the nose.
- Function: Houses many of the executive functions, making us human.
- Importance: Critical for concentration, planning, and problem-solving.
2. Parietal Lobe:
- Location: Just behind the frontal lobe.
- Function: Related to senses, mathematics, finding words, and writing words.
3. Temporal Lobe:
- Location: In green, comprising a large chunk.
- Function: Related to memory, impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease.
4. Occipital Lobe:
- Location: Way in the back.
- Function: Controls vision.
5. Cerebellum:
- Location: Below the occipital lobe.
- Importance: Critical to brain function.
- Regions: Includes the spinal cerebellum (balance), cerebral cerebellum, and vestibular cerebellum (dizziness, disorientation).
6. Basal Ganglia:
- Location: Deep in the brain.
- Function: Related to Parkinson’s disease and emotions.
Nervous System Components
1. Parasympathetic:
- Function: Helps in relaxation, digestion, and calming.
- Common Issues: Chronic digestive problems and constipation.
2. Sympathetic:
- Function: Fight or flight response.
- Common Issues: Anxiety, night sweats, sensitivities. Most clients experience sympathetic overdrive.
3. Seizure Activity:
- Understanding: Assesses how stable the brain is with respect to epileptic seizure activity or spontaneous neurological ignitions.
Conclusion
It’s important to remember that the neurons in your brain have to last your entire life. Unlike skin cells, neurons don’t heal if they are damaged. If you have any specific concerns about your brain health, it would be wise to schedule a Zoom call with a healthcare professional who can provide a customized, individualized plan to address your specific needs.
Take care, and feel free to reach out with any questions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The form helps identify potential areas of neuroinflammation or brain dysfunction by assessing symptoms linked to specific brain regions and nervous system components, guiding a targeted corrective plan.
It means your "fight or flight" nervous system is chronically overactive, which can manifest as anxiety, sensitivities, sleep issues, and an inability to relax or digest properly.
Unlike other cells, neurons do not regenerate. Protecting them from inflammation and damage is crucial for long-term brain health, as they must last your entire lifetime.